Financial Portfolio
It wouldn’t be wrong to say that an asset portfolio is a collection of investment tools and financial assets held by an individual, an investment firm, or a financial institution. One needs to become familiar with its fundamentals and the factors that influence it.
As far as a financial portfolio goes, it’s a collection of diversified assets owned by investors. But, the collection of financial assets might be valuables that range from stocks, funds, property, derivatives, bonds, and cash equivalents. People put money in such assets to produce revenue.
It likewise ensures that the original equity of asset or capital doesn’t erode. Depending on how an investment market works, people either manage their portfolios or seek the assistance of financial advisors for the same.
Financial experts claim that diversification is a vital concept of portfolio management.
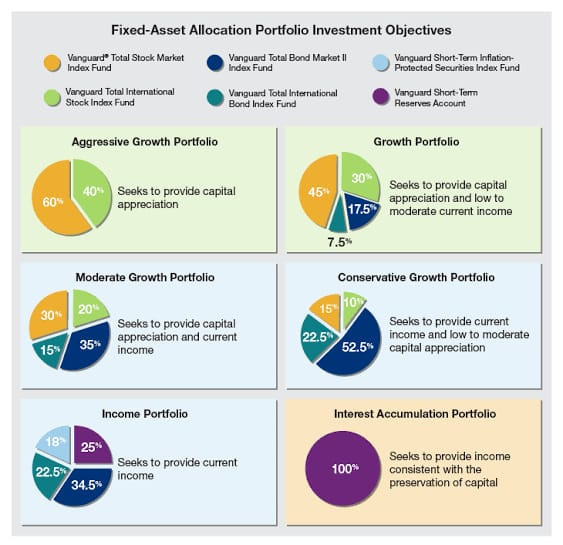
What are the components of a Financial Portfolio?
Stocks
Stocks refer to the investor’s ownership and company shares. The percentile of ownership depends on the number of stocks held by the person. The stockholders get a percentage of the company’s profits in terms of dividends.
Bonds
It is worth noting that a bond comes with a maturity date and is less risky than stocks. When it matures, investors get the principal investment amount alongside the interest.
Bonds form the risk-cushioning aspect of an investment portfolio.
Alternatives
Besides bonds and stocks, investors can also add investment instruments like real estate, oil, and gold.
Though there are multiple types of investment portfolios, investors make sure to build one that matches the risk capacity and investment intent.
Depending on the investment plans, here are the common types of a financial portfolio.
Income portfolio:
This type of portfolio focuses on securing a flow of income from investment schemes. In other terms, it doesn’t depend on potential capital appreciation. For instance, income-driven investors will invest in stocks that produce regular dividends rather than those who keep a track of the fall of value.
Growth-based portfolio
A growth-based portfolio depends on parks resources into a company’s growth stocks. Typically, a growth-based portfolio gets subjected to greater risks. This type of portfolio depends on presenting reward aspects and high risk.
Value-based portfolio
Such a portfolio puts funds into the valuation of cheap assets and focuses on securing bargains. When the economy falls down and companies are barely surviving, a value-based investor looks for profitable firms whose shares have a low price than their fair value.
If you know about the Asset Allocation. Do read this topic- WHAT IS ASSET ALLOCATION? AND HOW ITS WORKS?
From Hemant K Midha